Effective Treatments for Achilles Tendinitis
Imagine being at the peak of your athletic prowess, conquering every run, jump, and workout with ease, only to be suddenly halted by a nagging pain at the back of your heel. Or envisage the casual weekend hiker whose favorite trails have become a battleground against relentless discomfort. Achilles tendinitis can strike anyone, transforming routine activities into painful endeavors. This condition, caused by inflammation of the Achilles tendon, requires not just recognition but a well-rounded approach to treatment. In this article, we will explore effective treatments for Achilles tendinitis, equipping you with the knowledge to alleviate pain, promote healing, and reclaim your active lifestyle.
Rest and Activity Modification: The First Line of Defense
Achilles tendinitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the Achilles tendon, often caused by overuse or sudden increases in physical activity. The first line of defense in treating this condition is rest and activity modification. Resting the affected tendon is crucial to allow the inflammation to subside and prevent further injury. This means temporarily halting activities that exacerbate the pain, such as running, jumping, or any high-impact exercises. By giving the tendon time to heal, individuals can reduce pain and swelling, setting the stage for a more effective recovery process. It’s important to listen to one’s body and avoid pushing through the pain, as doing so can lead to more severe damage and prolong the healing period.
In addition to rest, modifying activities to include low-impact exercises can help maintain overall fitness while minimizing stress on the Achilles tendon. Activities such as swimming, cycling, or using an elliptical machine provide cardiovascular benefits without the high impact on the tendon. These alternatives allow individuals to stay active and maintain their fitness levels, which is essential for overall health and well-being. Gradually reintroducing more strenuous activities under the guidance of a healthcare professional ensures that the tendon is adequately prepared to handle increased loads. This gradual approach helps prevent re-injury and promotes long-term tendon health.
Moreover, incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises into the daily routine can aid in the recovery process. Gentle stretching of the calf muscles and Achilles tendon can improve flexibility, while strengthening exercises can enhance the resilience of the tendon and surrounding muscles. Eccentric exercises, where the muscle lengthens under tension, are particularly beneficial for tendon healing. These exercises should be done with proper technique and under professional supervision to avoid further injury. By prioritizing rest and activity modification, individuals with Achilles tendinitis can effectively manage their symptoms, promote healing, and reduce the risk of chronic issues, ultimately leading to a return to pain-free movement and activity.
Treatments for Achilles Tendinitis
Ice Therapy: Reducing Inflammation and Pain
Achilles tendinitis is a common condition marked by inflammation and pain in the Achilles tendon, typically caused by overuse or sudden increases in physical activity. One of the most straightforward and effective treatments for managing the symptoms of Achilles tendinitis is ice therapy. Applying ice to the affected area helps reduce inflammation and numb the pain, offering immediate relief. The cold constricts blood vessels, which decreases blood flow to the injured tissue, thereby reducing swelling and inflammation. Ice therapy is particularly beneficial during the acute phase of the injury, where controlling inflammation is crucial to prevent further damage and facilitate the healing process.
The application of ice therapy should be done with caution to avoid frostbite or skin damage. A common method involves wrapping ice packs or bags of frozen vegetables in a thin cloth or towel and applying them to the injured area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. This intermittent application allows sufficient time for the tissue to cool down and reduces the risk of cold-induced injury. Combining ice therapy with rest and elevation of the affected leg can enhance its effectiveness. Elevating the leg helps reduce blood flow to the area, working in conjunction with the cold to minimize swelling and alleviate discomfort.
In addition to providing immediate relief, regular use of ice therapy for Achilles tendon can significantly aid in the overall recovery from Achilles tendinitis. It helps manage pain levels, allowing individuals to engage in light activities and begin gentle stretching exercises sooner, which are essential for long-term recovery. Ice therapy is often used in combination with other treatments such as physical therapy, orthotics, and supportive footwear to provide a comprehensive approach to managing Achilles tendinitis. By incorporating ice therapy into their treatment regimen, individuals can effectively control pain and inflammation, setting the stage for a quicker and more complete recovery.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Pain Management
Achilles tendinitis is a condition marked by pain and inflammation of the Achilles tendon, commonly due to overuse or sudden increases in physical activity. One of the most effective treatments for managing the symptoms of Achilles tendinitis is the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These medications work by reducing inflammation and alleviating pain, making them a crucial component in the initial stages of treatment. NSAIDs can significantly improve comfort and mobility, allowing individuals to continue with their daily activities while the tendon heals. They are particularly useful in addressing acute flare-ups, where pain and swelling are most pronounced.
The mechanism of action for NSAIDs involves inhibiting the enzymes cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), which play a key role in the inflammatory process. By blocking these enzymes, NSAIDs effectively reduce the production of prostaglandins, compounds that mediate inflammation and pain. This reduction in prostaglandins leads to decreased swelling, less tenderness, and improved range of motion in the affected tendon. While NSAIDs are useful for short-term pain management, it is important to use them under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid potential side effects such as gastrointestinal issues or cardiovascular risks. Proper dosage and duration of use are essential to maximize benefits and minimize adverse effects.
In conjunction with other treatments like rest, physical therapy, and activity modification, NSAIDs can contribute to a comprehensive approach to managing Achilles tendinitis. Physical therapy focuses on stretching and strengthening exercises that improve tendon flexibility and resilience, while activity modification helps prevent further strain on the tendon. By integrating NSAIDs into this multi-faceted treatment plan, individuals can experience more rapid pain relief and a smoother recovery process. However, it is crucial to address the underlying causes of tendinitis to prevent recurrence. Understanding and adhering to a well-rounded treatment strategy ensures effective pain management and promotes long-term tendon health.
Achilles Tendinitis Treatments
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Restoring Flexibility and Strength
Achilles tendinitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the Achilles tendon, often results from overuse or sudden increases in physical activity. One of the most effective Achilles tendon treatments for this ailment involves incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises into the daily routine to restore flexibility and strength to the affected tendon. Stretching exercises focus on elongating the calf muscles and Achilles tendon, which can help reduce tension and improve range of motion. Simple stretches, such as the runner’s stretch or towel stretch, can be performed multiple times a day to gently loosen tight muscles and tendons. Consistent stretching helps alleviate stiffness, reduces pain, and prevents further injury by maintaining the tendon’s elasticity.
Strengthening exercises, particularly eccentric exercises, play a crucial role in the rehabilitation process for Achilles tendinitis. Eccentric exercises involve lengthening the muscle while it is under tension, which has been shown to promote tendon healing and increase its resilience. For example, heel drop exercises, performed by standing on the edge of a step and slowly lowering the heel below the step level, effectively target the Achilles tendon and calf muscles. These exercises should be done with proper technique and gradually increased in intensity to avoid exacerbating the injury. A well-structured strengthening program not only improves tendon strength but also enhances the overall stability and function of the ankle joint, reducing the risk of recurrence.
Combining stretching and strengthening exercises provides a comprehensive approach to treating Achilles tendinitis and ensures long-term recovery. It is essential to perform these exercises regularly and consistently, ideally under the guidance of a physical therapist or healthcare professional who can tailor the regimen to individual needs and monitor progress. In addition to enhancing flexibility and strength, these exercises help correct imbalances and improve overall biomechanics, contributing to better tendon health. By adhering to a structured exercise program, individuals with Achilles tendinitis can experience significant improvements in pain, mobility, and function, ultimately returning to their normal activities with greater confidence and reduced risk of future injuries.
Orthotics and Supportive Footwear: Enhancing Comfort and Stability
Achilles tendinitis is a persistent and painful condition that affects the tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. Effective treatment often includes the use of orthotics and supportive footwear, which play a vital role in enhancing comfort and stability for individuals suffering from this condition. Orthotic devices, such as custom-made insoles, are designed to provide optimal support to the foot’s arch and correct any biomechanical imbalances that may contribute to tendon strain. By redistributing pressure more evenly across the foot, orthotics can alleviate stress on the Achilles tendon, reducing pain and promoting healing. These devices are especially beneficial for individuals with flat feet or high arches, as they help maintain proper foot alignment during movement.
Supportive footwear is equally important in managing Achilles tendinitis. Shoes with appropriate cushioning and arch support can significantly reduce the impact on the Achilles tendon during everyday activities. Well-designed athletic shoes, for instance, often feature shock-absorbing soles and reinforced heel counters that provide additional stability and protection. Wearing shoes that fit well and offer adequate support can prevent excessive pronation or supination, which are common culprits in aggravating the Achilles tendon. Additionally, avoiding high heels or unsupportive footwear can further help in reducing strain on the tendon, making supportive shoes a critical component of both treatment and prevention strategies.
Combining orthotics with supportive footwear creates a synergistic effect that enhances overall foot comfort and tendon stability. This combination not only helps in alleviating existing symptoms but also plays a preventive role by minimizing the risk of further injury. For optimal results, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or podiatrist who can assess individual needs and prescribe the most suitable orthotic devices and footwear. By integrating these supportive measures into daily life, individuals with Achilles tendinitis can experience significant improvements in pain management, mobility, and overall function. This holistic approach ensures a more comfortable recovery journey and helps maintain long-term tendon health, allowing individuals to return to their normal activities with confidence and reduced risk of recurrence.
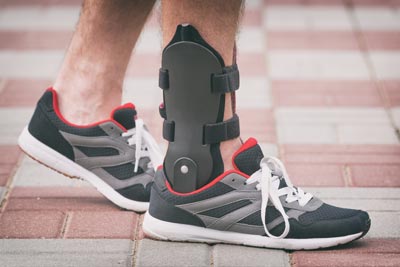
Orthotics for Achilles tendinitis
Physical Therapy: Professional Guidance for Optimal Recovery
Achilles tendinitis, characterized by pain and inflammation of the Achilles tendon, can be effectively managed through physical therapy. This professional approach offers tailored exercises and techniques designed to promote healing, improve mobility, and prevent recurrence. Physical therapists begin with a comprehensive assessment to determine the severity of the condition and identify any contributing factors such as muscle imbalances or improper biomechanics. Based on this evaluation, they develop a personalized treatment plan that may include a combination of stretching, strengthening, and manual therapy techniques. These targeted interventions help reduce pain and inflammation while restoring function to the affected tendon.
One of the key components of physical therapy for Achilles tendinitis is a structured exercise regimen. Stretching exercises focus on improving the flexibility of the calf muscles and Achilles tendon, thereby reducing tension and enhancing the range of motion. Strengthening exercises, particularly eccentric exercises where the muscle lengthens under load, are crucial in rebuilding tendon strength and resilience. These exercises help repair microtears in the tendon, stimulate collagen production, and enhance overall tendon health. Additionally, physical therapists may incorporate balance and proprioception activities to improve ankle stability, further protecting the tendon from future injuries.
Manual therapy techniques employed by physical therapists can also play a significant role in the recovery process. Techniques such as massage, joint mobilization, and myofascial release help to alleviate muscle tightness, improve blood flow, and reduce scar tissue formation. These hands-on methods complement exercise therapy by addressing soft tissue restrictions and enhancing the overall healing environment. Throughout the rehabilitation process, physical therapists provide education on proper footwear, activity modification, and injury prevention strategies. By adhering to a professionally guided physical therapy program, individuals with Achilles tendinitis can achieve optimal recovery, regain normal function, and return to their regular activities with reduced pain and a lower risk of future tendon issues.
Advanced Treatment Options: Exploring Beyond Conventional Methods
For individuals suffering from Achilles tendinitis, conventional treatment methods such as rest, stretching, and strengthening exercises are often effective. However, in cases where these approaches do not yield sufficient results, exploring advanced treatment options can provide additional relief and facilitate recovery. One such option is shockwave therapy, a non-invasive procedure that uses high-energy sound waves to stimulate healing in the affected tendon. This therapy promotes increased blood flow, reduces inflammation, and accelerates tissue repair by delivering targeted pulses of energy to the injured area. Shockwave therapy is particularly beneficial for chronic tendinitis, where the body’s natural healing process needs an extra boost to overcome persistent symptoms.
Another advanced Achilles tendinitis treatment option is platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, which involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s own blood directly into the damaged tendon. Platelets contain growth factors that play a crucial role in tissue repair and regeneration. By injecting a high concentration of these growth factors into the affected area, PRP therapy can enhance the body’s natural healing response and promote the regeneration of healthy tendon tissue. This treatment has gained popularity among athletes and active individuals seeking to expedite their recovery and return to peak performance. Although PRP therapy is minimally invasive, it should be administered by a qualified healthcare professional to ensure optimal results and minimize risks.
In addition to shockwave and PRP therapies, other advanced options such as laser therapy and stem cell therapy are also being explored for their potential benefits in treating Achilles tendinitis. Laser therapy uses focused light energy to reduce pain and inflammation while promoting cellular repair and tissue regeneration. Stem cell therapy, on the other hand, involves the injection of stem cells into the injured tendon to stimulate the growth of new, healthy tissue. Both therapies aim to harness the body’s natural healing mechanisms, offering promising alternatives for individuals who have not responded well to conventional treatments. By considering these advanced treatment options, patients with Achilles tendinitis can access a broader range of interventions, potentially achieving faster and more complete recovery outcomes.

Advanced Achilles tendinitis Treatment
Conclusion
Achilles tendinitis can be a daunting hurdle for anyone committed to an active lifestyle. However, understanding and implementing effective treatment strategies can facilitate recovery and prevent recurrence. By prioritizing rest, utilizing ice therapy, managing pain with NSAIDs, engaging in targeted exercises, using orthotics and supportive footwear, seeking physical therapy, and exploring advanced treatment options, you can address Achilles tendinitis comprehensively. Empower yourself with the knowledge and resources needed to overcome this condition and return to your favorite activities stronger than before. Here’s to a pain-free journey and a swift path to recovery!
Flagstaff Foot Doctors: Anthony Rosales DPM
https://www.google.com/maps?cid=8835841318590452161
421 N Humphreys St, Flagstaff, AZ 86001, United States
(928) 774-4825
https://flagstafffootandankle.com/
