Arthritis in Feet, Ankles, and Toes: Causes and Management
Arthritis in feet, a widespread ailment, impacts countless individuals globally. This condition arises due to inflammation in one or several joints, resulting in discomfort and reduced mobility. Although arthritis can target joints throughout the body, it most frequently affects the feet, ankles, and toes.
Understanding Arthritis in Lower Extremities
Arthritis in the lower extremities, particularly in the feet, ankles, and toes, poses unique challenges due to the constant demand placed on these areas for mobility and balance. The feet and ankles bear the body’s weight, and with every step, they absorb the impact of movements, which can exacerbate arthritis symptoms. Osteoarthritis, characterized by the wearing down of the protective cartilage within the joint, is the most common form affecting these regions. However, rheumatoid arthritis and gout can also significantly impact the lower extremities, leading to acute pain and mobility issues. Early diagnosis and management are crucial in mitigating the symptoms and improving the quality of life for those suffering from arthritis in these crucial joints.
Arthritis in Feet Treatment
Causes of Arthritis in Feet, Ankles, and Toes
- Osteoarthritis:Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis affecting the joints in feet, ankles, and toes. It is characterized by the degeneration of cartilage, the flexible and protective tissue at the ends of bones. This deterioration leads to bones rubbing against each other, causing pain, swelling, and restricted movement. Factors contributing to the development of osteoarthritis in these areas include age, obesity, previous injury, and repetitive stress on the joints from activities or occupations that involve prolonged standing or walking.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is another prevalent form of arthritis that can severely affect the feet, ankles, and toes. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is primarily a degenerative disease, RA is an autoimmune disorder. In RA, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joint’s lining, leading to inflammation, pain, and in severe cases, joint deformity. This chronic inflammation can damage cartilage and bone within the joint, causing long-term discomfort and disability. RA is more common in women than men and can occur at any age, although it frequently begins in middle age. Lifestyle adjustments, medication, and sometimes surgery are required to manage the symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
- Gout: Gout represents a form of inflammatory arthritis, triggered by the accumulation of uric acid crystals within various joints. This condition often affects the feet, ankles, and toes, leading to intense pain and significant swelling.
Management of Arthritis in Feet, Ankles, and Toes
While there is no cure for arthritis, there are various management strategies that can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include:
- Medications: A key component in managing arthritis in the feet, ankles, and toes involves the use of medications designed to reduce pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to alleviate discomfort and swelling. For more severe cases, especially those involving rheumatoid arthritis, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be recommended. DMARDs can slow the progression of RA and prevent joint and tissue damage. Additionally, corticosteroids, either taken orally or injected directly into the affected joint, can offer fast relief by reducing inflammation quickly. It’s crucial for patients to discuss the potential benefits and side effects of these medications with their healthcare provider to ensure the most effective and safe treatment plan.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy emerges as a vital component in managing arthritis in the feet, ankles, and toes. A tailored physical therapy program, developed in conjunction with a certified physical therapist, can significantly enhance joint mobility, strength, and overall function. Exercises focusing on stretching and strengthening the muscles around the affected joints can reduce the strain on those joints, improving stability and reducing pain. Additionally, physical therapists may employ techniques such as ice and heat therapy, ultrasound, or electrical nerve stimulation to further alleviate pain and inflammation. Engaging in regular physical therapy sessions can empower individuals with arthritis to maintain their range of motion, decrease discomfort, and potentially slow the progression of the condition.
- Orthotic Devices: The application of orthotic devices is another effective strategy for managing arthritis in the feet, ankles, and toes. Custom-made or over-the-counter orthotics provide support, reduce pressure on affected joints, and can help redistribute weight in the foot area. By correcting the alignment and improving the function of the feet and ankles, these devices can significantly lessen pain, enhance mobility, and prevent further joint damage. Orthotics come in various forms, including insoles, braces, and specialized footwear, tailored to address specific needs and symptoms of arthritis patients. It’s imperative for individuals to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable orthotic option for their condition, ensuring both comfort and therapeutic effectiveness.
Arthritis Management
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing the symptoms of arthritis in the feet, ankles, and toes. Making intentional changes to daily habits can significantly reduce stress on joints, alleviate pain, and improve overall well-being. Key lifestyle changes include maintaining a healthy weight to ease the pressure on lower-body joints, engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling to enhance joint flexibility without exacerbating pain, and adopting a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods to support joint health. Additionally, individuals with arthritis should avoid activities that overstrain the joints, such as running on hard surfaces or engaging in high-impact sports, and consider techniques for stress management, as stress can intensify pain perception. By incorporating these adjustments, people with arthritis can lead more active and comfortable lives, despite their condition.
Surgical Interventions for Arthritis
For individuals experiencing advanced stages of arthritis, particularly when previous treatment options have been ineffective, considering surgical procedures may be advisable. These procedures can include the replacement of affected joints with prosthetic ones or the fusion of specific bones, aimed at minimizing discomfort and enhancing the functionality of the joint.
Living with Arthritis in Feet, Ankles, and Toes:
Arthritis can have a significant impact on daily life, but with proper management and self-care, it is possible to live a fulfilling and active life. Some additional tips for managing arthritis in the feet, ankles, and toes include:
- Stretching exercises to improve flexibility
- Low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling
- Using heat or ice to alleviate pain and inflammation
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods
- Taking breaks and resting when needed
Identifying the Symptoms of Arthritis in Feet, Ankles, and Toes:
Recognizing the initial symptoms of arthritis in the feet, ankles, and toes is crucial for early intervention and effective management of the condition. Common signs include persistent foot pain or tenderness in one or multiple joints, swelling and inflammation around the joints, stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity, and a reduced range of motion. Some individuals may also experience a sensation of warmth in the affected areas or notice changes in the skin, such as redness. Over time, these symptoms can lead to difficulties in walking, climbing stairs, or performing other daily activities, significantly impacting one’s quality of life. If these symptoms are observed, consulting a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan is imperative.
Symptoms of Arthritis
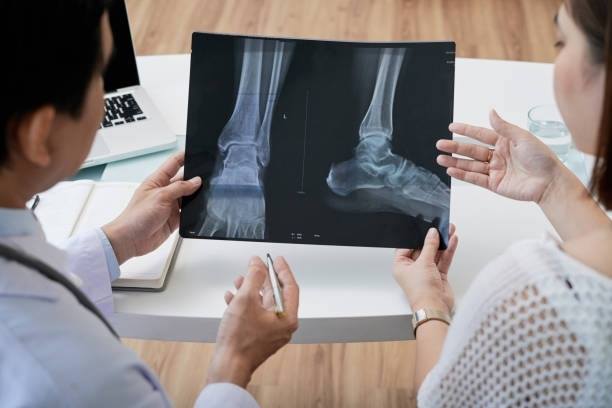
Diagnosis Procedures for Arthritis in Feet, Ankles, and Toes:
The process of diagnosing arthritis in the feet, ankles, and toes involves a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and advanced diagnostic tests. Initially, a foot healthcare professional will conduct a thorough physical examination, looking for signs of swelling, redness, warmth, and deformation in the affected joints. Patients will be asked about their symptoms, including their duration, severity, and any activities that exacerbate or alleviate them.
To confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the disease, imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and ultrasound may be utilized. These tests provide detailed images of the bones and soft tissues, revealing any joint damage, erosion, or evidence of inflammation. Additionally, blood tests might be ordered to identify markers of inflammation or specific antibodies associated with certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
In some cases, a joint aspiration procedure, where fluid is extracted from the affected joint using a fine needle, can be performed. Analyzing this fluid can help rule out other conditions, such as gout or infection, and confirm the presence of arthritis. Through these comprehensive diagnostic procedures, healthcare providers can determine the specific type of arthritis affecting the patient, guiding the development of a personalized and effective treatment plan.
Conclusion
In sum, arthritis in the feet, ankles, and toes presents a multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive approach for effective management. From employing supportive devices like orthotics to making crucial lifestyle modifications, and considering surgical interventions when necessary, individuals can adopt a variety of strategies to mitigate symptoms. Early recognition of symptoms, followed by accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment, plays a critical role in maintaining mobility, reducing pain, and enhancing the quality of life for those affected by this condition. With persistent efforts and a proactive approach towards health, living with arthritis in the lower extremities can be managed successfully, allowing individuals to lead active and fulfilling lives.
Flagstaff Foot Doctors: Anthony Rosales DPM
https://www.google.com/maps?cid=8835841318590452161
421 N Humphreys St, Flagstaff, AZ 86001, United States
(928) 774-4825
https://flagstafffootandankle.com/
