Understanding Ankle Pain: Causes and Treatment Options
Does ankle pain frequently slow you down? You’re not alone. Ankle pain is a common complaint that can significantly impact your daily life. Understanding its causes and knowing effective treatment options can help you get back on your feet—literally.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the reasons behind ankle pain, explain the diagnostic process, review various treatment options, and offer tips for prevention. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to manage and prevent ankle pain effectively.
What is Ankle Pain?
Ankle pain is a general term that describes discomfort or pain in the ankle region, which includes the area where the lower leg meets the foot. This pain can range from mild to severe and can be acute or chronic. Ankle pain is often a result of injuries, such as sprains or fractures, but it can also be caused by medical conditions like arthritis, tendonitis, or nerve compression. Identifying the cause of ankle pain is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Ankle pain is highly prevalent and affects people of all ages and activity levels. Athletes, in particular, are at increased risk due to the demands of their sports activities. However, anyone can experience ankle pain from routine activities or underlying health conditions. Seeking appropriate treatment is essential to avoid long-term complications and to ensure a swift recovery. Early diagnosis and intervention can not only relieve pain but also prevent future occurrences, helping individuals maintain their mobility and quality of life.

Ankle Pain Treatment
Common Causes of Ankle Pain
Ankle pain can originate from a variety of sources, each contributing to the discomfort in different ways. Here are some of the most common causes:
- Ankle Sprains: Ankle sprains are one of the most frequent causes of ankle pain. They occur when the ligaments that support the ankle stretch or tear, typically due to an unnatural twisting motion. Sprains can range from mild, involving slight stretching of the ligaments, to severe, where complete tears occur.
- Fractures: Ankle fractures involve a break in one or more of the bones that constitute the ankle joint. This type of injury often results from high-impact activities or accidents. Symptoms include immediate and severe pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the ankle.
- Arthritis: Arthritis, particularly osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, is a common cause of chronic ankle pain. Osteoarthritis involves the wear and tear of cartilage, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition causing inflammation in the joints.
- Tendonitis: Tendonitis refers to the inflammation of the tendons around the ankle joint. This condition often results from overuse or repetitive strain and is commonly seen in athletes and active individuals.
- Nerve Compression: Nerve compression, such as tarsal tunnel syndrome, occurs when nerves near the ankle become pinched or compressed. This can result in pain, numbness, or tingling sensations in the foot and ankle.
- Bursitis: Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between bones and soft tissues. Bursitis can develop from repetitive motion or prolonged pressure on the ankle.
Understanding these common causes can aid in the early identification and treatment of ankle pain, allowing individuals to seek the appropriate care and improve their recovery outcomes.
Understanding the Diagnostic Process for Ankle Pain
Identifying the root cause of ankle pain requires a thorough diagnostic process, which typically involves several steps. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional can determine the exact cause and guide the appropriate treatment plan. Here’s what to expect during the diagnostic process:
- Medical History: The first step often involves a detailed medical history review. Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, previous injuries, current medications, and any underlying health conditions. They may inquire about the circumstances leading to the onset of pain and any specific activities that exacerbate or alleviate your symptoms.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination is crucial to identifying visible signs of injury or abnormalities. The healthcare provider will inspect the ankle for swelling, bruising, deformities, and range of motion. They may also palpate (feel) the area to pinpoint the location of pain and check for tenderness.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are often necessary to get a clearer view of the structures within the ankle. Common imaging tests include:
- X-rays: Useful for detecting fractures, dislocations, and degeneration of the bones.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, including ligaments, tendons, and cartilage, helping to identify tears or inflammation.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Offers a more comprehensive view of the bone structures and can be particularly beneficial in complex cases.
- Ultrasound: Helps in visualizing soft tissues and is useful for diagnosing conditions such as tendonitis or bursitis.
Laboratory Tests
In certain cases, laboratory tests may be conducted to check for underlying medical conditions that could contribute to ankle pain. For example, blood tests can detect markers of inflammation, autoantibodies related to rheumatoid arthritis, or infections.
Special Tests and Procedures
Depending on the initial findings, your healthcare provider may perform additional tests or procedures for a more accurate diagnosis. These could include:
- Joint Aspiration: Removing a small amount of fluid from the joint for analysis, which can help diagnose infections or types of arthritis.
- Nerve Conduction Studies and Electromyography (EMG): Assess the function of nerves and muscles if nerve compression or damage is suspected.
By systematically going through these steps, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose the cause of ankle pain and create an effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Early and precise diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and fast recovery.
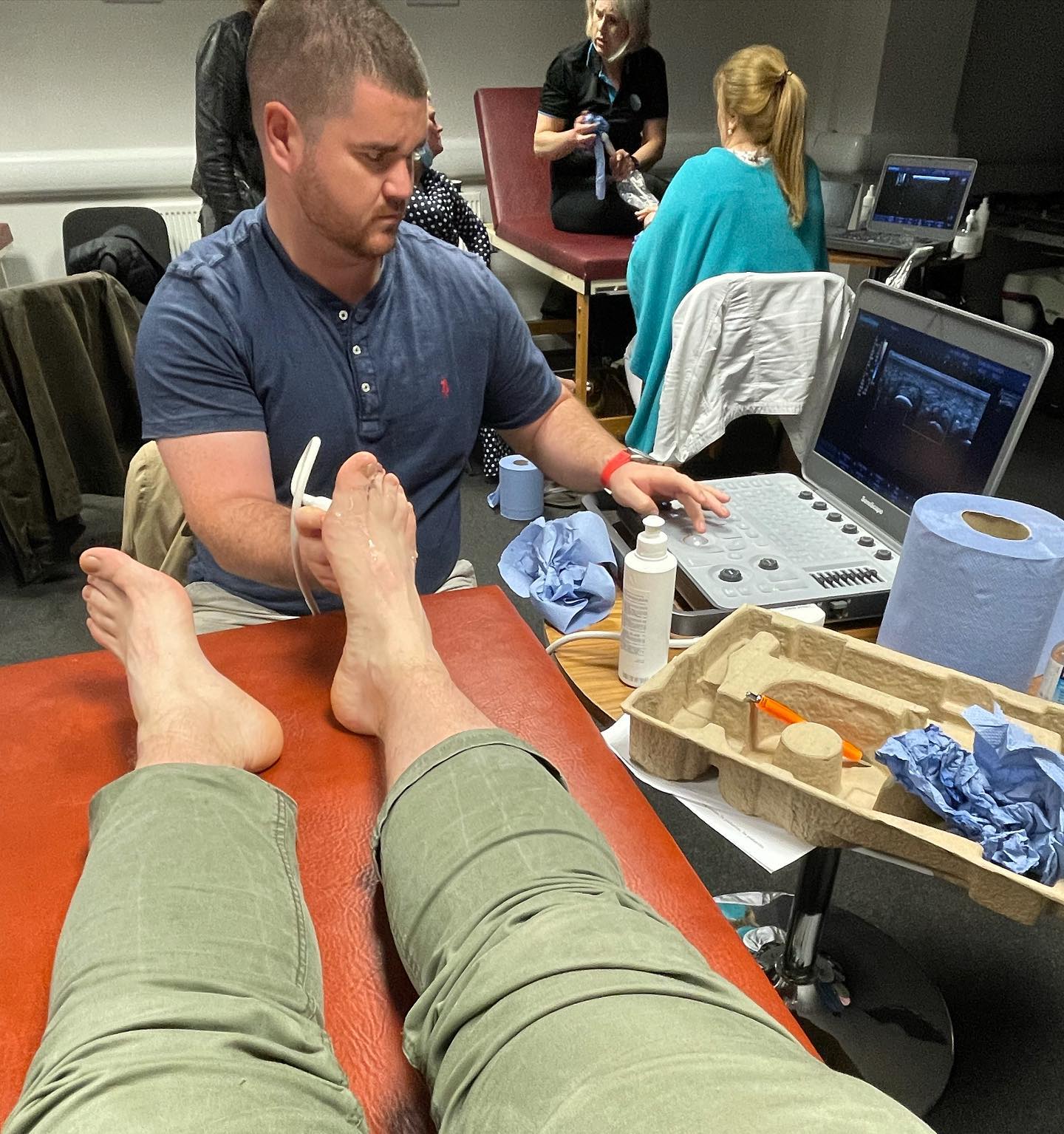
Diagnosing Ankle Pain
Treatment Options for Ankle Pain
Effective treatment of ankle pain depends on the underlying cause, severity of the condition, and individual patient factors. Here are some common treatment options:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE): This first-line treatment is effective for many minor injuries such as sprains and mild tendonitis. Resting the ankle, applying ice to reduce swelling, compressing the area with an elastic bandage, and elevating the foot above heart level can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In cases of severe pain or inflammation, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications such as corticosteroids or recommend specific pain management strategies.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a critical role in the rehabilitation of ankle injuries. Therapists can design tailored exercise programs to improve strength, flexibility, and stability. Techniques such as ultrasound therapy, electrical stimulation, and manual therapy may also be utilized to expedite recovery.
- Immobilization: For more serious injuries, such as fractures or severe sprains, immobilization may be required. This could involve the use of braces, splints, or casts to prevent movement and allow proper healing of the affected structures.
- Surgical Intervention: Surgery may be necessary for complex fractures, torn ligaments, or severe cases of arthritis that do not respond to conservative treatments. Common surgical procedures include ankle arthroscopy, ligament repair, and joint fusion. Post-surgical rehabilitation is crucial for a successful recovery.
- Orthotics and Braces: Custom orthotic devices and ankle braces can provide additional support, reduce pain, and prevent further injury. These are particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic conditions such as arthritis or those recovering from surgery.
- Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections can be administered directly into the ankle joint to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections are another option, helping to promote healing by utilizing the patient’s own blood components.
- Lifestyle and Home Remedies: Maintaining a healthy weight, wearing appropriate footwear, and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain can help manage and prevent ankle discomfort. Simple home exercises and stretches can also strengthen the ankle and improve mobility.
By employing an appropriate combination of these treatment options based on the specific cause and severity of the ankle pain, individuals can achieve relief and return to their normal activities with minimal risk of recurrence.
Preventing Ankle Pain
Preventing ankle pain involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, strength training, and awareness of potential risk factors. Here are some strategies you can implement to minimize the risk of ankle injuries:
- Wear Proper Footwear: Choosing shoes that offer adequate support and fit well can significantly reduce the risk of ankle injuries. Athletic shoes should be specific to the sport you are engaging in, providing the necessary cushioning and stability.
- Warm-Up and Stretch: Prior to any physical activity, it is crucial to engage in a proper warm-up followed by stretching exercises. This helps to increase blood flow to the muscles and improve flexibility, thus reducing the likelihood of sprains and strains.
- Strengthening Exercises: Incorporate foot and ankle exercises that specifically target the muscles around the ankle and foot. Strengthening these muscles can enhance stability and reduce the risk of injury. Balance exercises, such as standing on one foot, can also improve proprioception and prevent falls.
- Avoid Uneven Surfaces: Be cautious when walking or running on uneven or slippery surfaces. These conditions can increase the chances of rolling an ankle or sustaining an injury. Whenever possible, choose flat, stable surfaces for your activities.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any signs of pain or discomfort in your ankles. Ignoring early symptoms can lead to more severe injuries. If you experience consistent pain, it is advisable to seek medical advice to address any underlying issues.
- Gradual Progression: When increasing the intensity or duration of your physical activities, do so gradually. Sudden increases in activity levels can place additional stress on your ankles and elevate the risk of injuries.
- Use Supportive Devices: For individuals with a history of ankle injuries or those participating in high-risk sports, using supportive devices like ankle braces or taping can provide extra stability and prevent further damage.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine and being mindful of your ankle health, you can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing ankle pain and injuries.

Ankle Pain Management and Care
When to Seek Medical Attention for Ankle Pain
Knowing when to seek medical attention for ankle pain is crucial for preventing further injury and promoting proper healing. Here are some indicators that professional help is needed:
- Persistent Pain: If ankle pain persists for more than a few days even after initial home treatment, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider. Chronic pain can indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires medical evaluation and treatment.
- Severe Swelling and Bruising: Severe or worsening swelling and bruising that does not subside with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) should prompt a visit to a doctor. Significant swelling can indicate a fracture or torn ligament.
- Inability to Bear Weight: If you are unable to bear weight on the affected ankle or experience significant difficulty walking, it is important to seek medical advice. This may suggest a serious injury such as a fracture or severe sprain that needs immediate attention.
- Deformity: Visible deformity or misalignment in the ankle area is a clear sign to seek urgent medical attention. This could be indicative of a dislocation or complex fracture that requires prompt intervention.
- Redness and Warmth: Redness, warmth, and tenderness around the ankle joint, especially when accompanied by fever, could suggest an infection or inflammatory condition. It is important to seek medical evaluation to address any potential systemic issues.
- Lack of Improvement: If there is no significant improvement in ankle pain and function despite following conservative treatment methods for a reasonable period, visiting a healthcare professional is necessary. Persistent symptoms may need further diagnostic tests and specialized treatment.
- Instability: Experiencing a feeling of instability or weakness in the ankle, especially after an injury, needs medical attention. Chronic instability can lead to recurrent injuries and may require targeted rehabilitation or surgical intervention.
By recognizing these signs and seeking timely medical care, individuals can ensure proper diagnosis and effective ankle treatment, thereby reducing the risk of long-term complications and promoting a swift recovery.
Conclusion
Ankle pain can be a common and debilitating problem for many individuals. However, with proper management and preventive measures, it is possible to reduce the risk of experiencing ankle pain and promote optimal healing. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, incorporating strengthening exercises, and being mindful of potential risk factors, individuals can take control of their ankle health and continue to lead an active life without the limitations of ankle discomfort. Additionally, knowing when to seek medical attention for persistent or severe symptoms is crucial in preventing further injury and ensuring timely treatment. With proper care and awareness, individuals can effectively manage ankle pain and maintain strong, stable ankles for a lifetime.
Flagstaff Foot Doctors: Anthony Rosales DPM
https://www.google.com/maps?cid=8835841318590452161
421 N Humphreys St, Flagstaff, AZ 86001, United States
(928) 774-4825
https://flagstafffootandankle.com/
