Exploring the Anatomy of Foot Bones: A Comprehensive Guide
The human foot is a marvel of evolution and engineering, a complex structure that serves as the foundation of our every move. Most people will walk over 100,000 miles in their lifetime, subjecting the 26 bones and a sophisticated network of ligaments, muscles, and tendons in each foot to a significant amount of strain. Understanding this foundation is crucial not only for athletes and healthcare professionals but also for anyone who values mobility and health. In this exploration, we’ll take you through the intricacies of foot bone anatomy, common foot conditions, the significance of foot health, and practical tips to keep you on your toes – quite literally.
The Basics: Foot Bone Fundamentals
The human foot comprises three major segments – the forefoot, midfoot, and hindfoot – and each of these segments contains a particular group of bones that contribute to the various functions of the foot, from balance and propulsion to maintaining an arch structure. In the forefoot, five metatarsal bones are connected to the toes by joints and ligaments, supporting weight and allowing movement. Midfoot bones, including the navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms, create the arch of the foot, a critical shock absorber during walking. Finally, the hindfoot, primarily represented by the talus and calcaneus (heel bone), assists in locomotion and acts as a lever for the calf muscles during running or jumping.
Learning about the function of these bones provides insight into the mechanics of movement. For instance, take the metatarsals, which are longer and more rigid than the tarsal bones. They help the foot to push off the ground and propel the body forward. Understanding this specialized function can illuminate the causes and treatments of conditions like metatarsalgia, an inflammation that typically affects the ball of the foot.
Anatomy of Foot Bones
Common Foot Conditions and Foot Bones
Common foot conditions often arise from overuse, injury, or structural abnormalities affecting the bones in the foot. These conditions can range from mild discomfort to significant impairment, impacting one’s quality of life. Among the most prevalent issues related to the foot bones are plantar fasciitis, stress fractures, bunions, and arthritis.
- Plantar Fasciitis: This condition is characterized by pain in the heel and bottom of the foot, primarily caused by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue connecting the heel bone to the toes. Overuse, excess weight, or inadequate footwear can strain the plantar fascia, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Stress Fractures: These small breaks in the foot bones often result from repetitive force, overuse, or osteoporosis. The metatarsal bones are particularly susceptible to stress fractures due to the high pressure and impact they endure during activities like running or jumping.
- Bunions: A bunion forms when the big toe pushes against the next toe, causing the joint of the big toe to enlarge and protrude. The condition can lead to discomfort and pain as the bunion becomes more prominent. Factors contributing to bunion development include genetic predisposition and improper footwear.
- Arthritis: Foot arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation and pain in the foot joints. The most common type affecting the foot is osteoarthritis, which results from the wear and tear of joint cartilage, especially in the ankle and the big toe joints. Rheumatoid arthritis and gout can also affect the feet, causing significant pain and mobility issues.
Understanding the relationship between specific foot bones and these common conditions is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. For example, recognizing the role of the metatarsal bones in stress fractures can aid in identifying the signs and symptoms of this condition. Addressing foot health proactively by wearing appropriate footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, and incorporating foot exercises can help mitigate the risk of developing these conditions.
The Importance of Foot Health
Maintaining optimal foot health is vital for overall well-being and the ability to engage in daily activities with ease and comfort. The feet are the body’s foundation, supporting its weight and enabling mobility and balance. Neglecting foot health can lead to a cascade of issues, including impaired posture, altered gait, and even chronic conditions related to other parts of the body such as the knees, hips, and back. Furthermore, poor foot health can significantly impact one’s quality of life by limiting mobility, making it difficult to exercise, and participating in social activities, which are crucial for mental health and well-being.
Proactive foot care, including regular checks for abnormalities, wearing well-fitted shoes, and performing foot-specific exercises, can prevent many common foot problems. For those with existing conditions, understanding the anatomy and functions of the foot bones—as discussed earlier—can be instrumental in seeking appropriate treatment and managing symptoms effectively. Healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of foot health in preventative medicine, highlighting that taking care of our feet is an investment in our overall health.
Understanding Foot Strain and Injuries
Understanding foot strain and injuries is essential for prevention and proper management. The foot’s complex structure makes it particularly susceptible to strain and injuries, which can arise from everyday activities, sporting endeavors, or accidental incidents. Strains commonly occur when the foot’s muscles or tendons are stretched beyond their normal capacity, leading to pain, swelling, and difficulty in movement. These injuries are often seen in individuals who engage in high-impact sports or those with occupations requiring prolonged standing or walking.
Injuries to the foot can range from minor bruises and cuts to more severe conditions such as fractures, dislocations, and ligament tears. Fractures can affect any of the bones in the foot and vary in severity from small cracks to complete breaks, necessitating varying degrees of medical attention and recovery time. Dislocations occur when the bones in a joint are forced out of alignment, often causing immediate and severe pain, while ligament tears, resulting from sudden twists or excessive force, can lead to long-term instability and discomfort.
Preventative measures such as wearing appropriate footwear, maintaining flexibility and strength through regular exercises, and listening to the body’s signals can significantly reduce the risk of foot strains and injuries. In cases where injuries do occur, it is crucial to seek prompt medical advice to ensure a proper diagnosis and effective treatment plan. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are often recommended as initial treatment steps for managing inflammation and pain. However, more severe injuries may require physical therapy, medication, or even surgery to ensure a full recovery and return to normal function. Understanding the risks and appropriate responses to foot strain and injuries is a vital component of maintaining foot health and overall physical well-being.
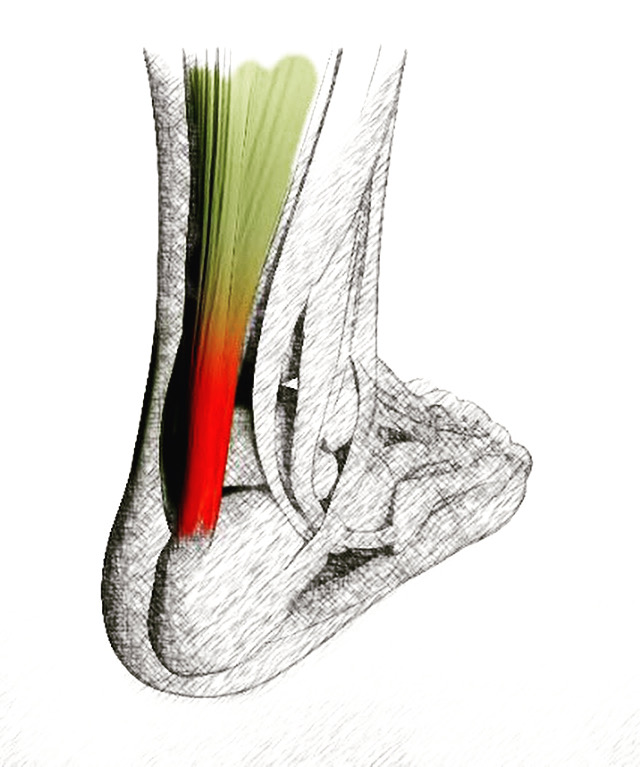
Anatomy of Foot Bones
Protecting Your Feet: Tips for Proper Foot Care
Taking steps to protect and care for your feet can prevent numerous foot-related problems and ensure your mobility and comfort. Here are some essential tips for maintaining healthy feet:
- Wear the Right Shoes: Choose footwear that fits well and provides appropriate support for your foot arch and heel. Avoid wearing high heels or tight shoes for extended periods, as they can lead to bunions, hammertoes, and other foot issues.
- Keep Your Feet Dry: Moisture can create an environment for fungal infections like athlete’s foot. After washing, thoroughly dry your feet, especially between the toes.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your feet daily with soap and water. This simple routine can prevent infections and eliminate odor.
- Trim Toenails Properly: Cut your toenails straight across and avoid cutting too close to the skin. This method helps prevent ingrown toenails.
- Moisturize: Apply a good quality foot cream or moisturizer to prevent dry skin and cracks, particularly on the heels.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise promotes good circulation in your feet. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are excellent for foot health.
- Monitor Your Feet: Regularly check your feet for cuts, sores, blisters, or any changes in color or temperature. Early detection of potential issues is key to minimizing complications.
- Avoid Walking Barefoot: Especially in public areas, walking barefoot increases your risk of injury and infection.
- Consider Orthotics: If you have specific foot issues, custom orthotics prescribed by a podiatrist can provide additional support and alleviate discomfort.
- Schedule Regular Check-ups: Those with diabetes or other conditions that affect foot health should have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to prevent and treat foot problems promptly.
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can significantly improve your foot health, ensuring that your feet remain strong and free from pain, allowing you to stay active and enjoy a high quality of life.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Maintaining Healthy Feet
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of your feet, especially for individuals recovering from injuries or surgeries, and those looking to prevent foot-related problems. A physical therapist can develop a personalized plan that includes exercises aimed at strengthening the foot muscles, enhancing flexibility, and improving range of motion. Such exercises not only aid in recovery but also help in preventing future injuries by stabilizing the foot and ankle, correcting imbalances, and improving proprioception — your body’s ability to perceive its position in space.
In addition to exercise, physical therapists employ various techniques to alleviate foot pain and dysfunction. Manual therapy techniques, such as massage and joint mobilization, can reduce pain, decrease inflammation, and increase mobility. For individuals with specific conditions like plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendonitis, modalities like ultrasound therapy or electrical stimulation might be used to promote healing and relieve discomfort.
Physical therapists also play a vital role in educating patients on proper foot care and the selection of appropriate footwear. They can provide guidance on the types of shoes that will offer the necessary support for an individual’s unique foot structure and the activities they engage in. This educational aspect is crucial for not only addressing existing foot issues but also preventing new ones from arising.
Ultimately, physical therapy can be a gateway to more active and pain-free living, enabling individuals to continue or return to their desired activities without the limitations imposed by foot discomfort or injury.
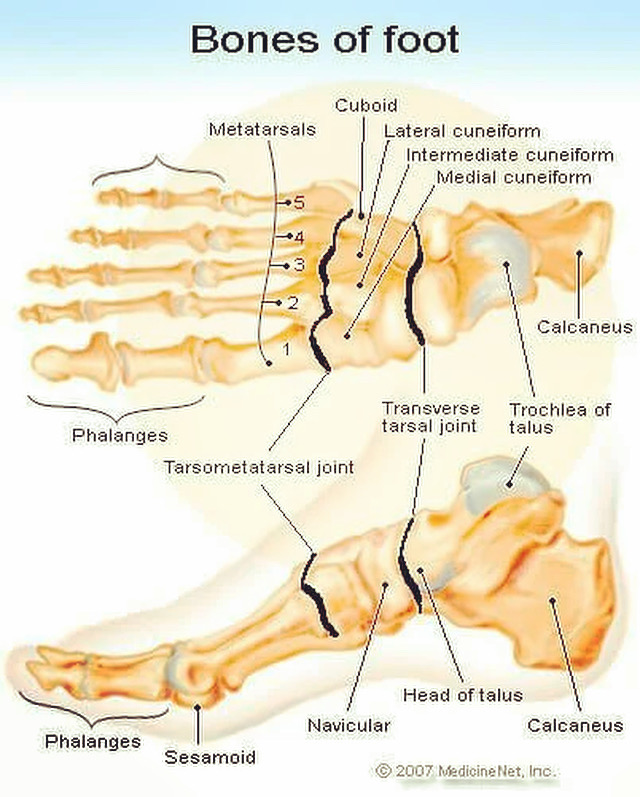
Anatomy of Foot Bones
Prevention and Treatment of Foot Problems
Proactively addressing foot health through prevention and when needed, prompt treatment, significantly improves quality of life and mobility. Engaging in prevention strategies minimizes the risk of developing foot problems, while effective treatment ensures a speedy return to daily activities and reduces the likelihood of future issues.
Preventive Care: To avoid common foot issues, including strain injuries, fungal infections, and deformities, incorporating good foot care practices into one’s daily routine is essential. Wearing properly fitting shoes, maintaining foot hygiene, and incorporating foot-strengthening exercises can all contribute to healthier feet. Additionally, understanding and mitigating risk factors, such as managing diabetes effectively or avoiding repetitive stress on the feet, play a crucial role in foot health.
Treatment Approaches: When foot problems arise, treatment should be timely and tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Over-the-counter remedies and conservative treatments, such as anti-inflammatory medications, rest, and ice, can be effective for minor issues. More significant problems may necessitate medical interventions, including physical therapy, prescription medications, or surgery. Custom orthotic devices can provide support for specific conditions, offering relief and preventing further damage. In all cases, consulting with a healthcare provider or a foot care specialist ensures that the treatment plan is appropriate and that any underlying issues are addressed.
Collaborative Care: Often, the most successful approach to managing foot problems involves a collaborative effort among various healthcare professionals. Podiatrists, orthopedists, physical therapists, and primary care physicians can all contribute their expertise. For individuals with chronic conditions affecting the feet, such as diabetes, this multidisciplinary approach is particularly crucial to prevent complications and maintain overall foot health.
By prioritizing prevention and seeking appropriate treatment when necessary, individuals can maintain their foot health, supporting their overall wellbeing and enabling them to lead active, fulfilling lives.
In conclusion, maintaining foot health is crucial for overall wellbeing and quality of life. Incorporating good foot care practices, monitoring your feet regularly, and seeking appropriate treatment when needed can all contribute to healthier feet. Physical therapy plays a vital role in promoting foot health through exercise, manual techniques, education, and collaborative care with other healthcare professionals. By prioritizing prevention and taking prompt action when foot problems arise, individuals can continue to engage in their desired activities without the limitations of pain or discomfort. Remember to always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and care to ensure you are taking proper care of your feet and preventing any potential issues. With these tips in mind, you can keep your feet healthy and strong, supporting an active and fulfilling lifestyle.
Flagstaff Foot Doctors: Anthony Rosales DPM
https://www.google.com/maps?cid=8835841318590452161
421 N Humphreys St, Flagstaff, AZ 86001, United States
(928) 774-4825
https://flagstafffootandankle.com/
